Link to paper
The full paper is available here.
You can also find the paper on PapersWithCode here.
Abstract
- Large language models have reignited debate about whether human cognitive capacities can emerge from them.
- Of particular interest is the ability of these models to reason about novel problems without training.
- A comparison was made between human reasoners and a large language model on a range of analogical tasks.
- The language model displayed a strong capacity for abstract pattern induction, matching or surpassing human capabilities.
Paper Content
Introduction
- Analogical reasoning is an important part of human intelligence and creativity
- Tests of analogical reasoning ability measure fluid intelligence
- Recent research has focused on training neural networks on analogy problems
- An alternative approach uses large language models (LLMs)
- LLMs can perform few-shot and zero-shot reasoning
- GPT-3 was evaluated on zero-shot analogy tasks and compared to human behavior
- GPT-3 performed as well or better than humans in most conditions
Results
- GPT-3 is a language model with 175 billion parameters
- It was trained on a web-based corpus of natural language
- It was trained using two objectives
- We evaluated GPT-3 on analogy tasks, letter string analogies, and four-term verbal analogies
- We also performed a qualitative evaluation on a problem-solving task
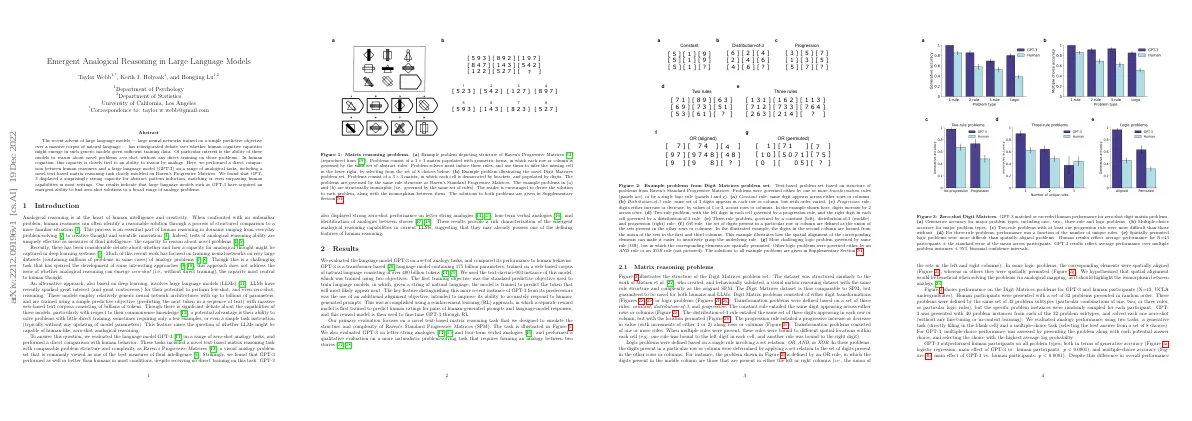
Matrix reasoning problems
- Digit Matrices problem set is structured similarly to Matzen et al.
- Consists of digit transformations and logic problems
- Transformation problems defined by 3 rules: constant, distribution-of-3, and progression
- Logic problems defined by single rule involving set relation: OR, AND, or XOR
- GPT-3 outperformed human participants on all problem types
- Performance levels similar across problem subtypes
- Problems with progression rules more difficult
- Problem difficulty driven by number of unique relations
- Analogical mapping easier when more constraints support correct mapping
- Digit Matrices text-based format may not engage same processes as visual format
- Performance similar across one-rule, two-rule, and logic problems
- Performance improved when presented with problems in order of increasing complexity
- GPT-3 benefited from contextual information, but also impaired by it
Letter string analogies
- Presented letter string analogies to GPT-3
- Evaluated GPT-3 without prompt and on alternative format
- Generated multiple instances by varying letters used in target
- 18 basic successor relation problems
- 16 problems involving removal of redundant character
- 6 letter-to-number problems
- 18 grouping problems
- 16 problems with longer target
- 17 successor-to-predecessor problems
- 17 problems used as context to test for relational priming
Four-term verbal analogies
- Evaluated GPT-3 on UCLA-VAT dataset
- Used colon notation for problems
- Each problem had two answer choices
- GPT-3 was presented with problem and answer choice
- Log probability used to select answer choice
Analogy in natural language problem-solving
- Analogical reasoning is important in real-world problem-solving
- GPT-3 was tested on naturalistic analogy problems based on stories
- GPT-3 was able to identify the solution to the target problem when presented with the source story
- GPT-3 was able to explain the analogy and identify the correspondences between the source story and target problem
- GPT-3 was less successful when presented with distracting, non-analogous stories
- GPT-3 was able to identify the analogy when prompted
- GPT-3 was not able to use the analogy to discover an appropriate solution due to lack of physical reasoning skills
Discussion
- GPT-3 displays an emergent ability to reason by analogy
- GPT-3 outperformed human participants on a novel text-based problem set
- GPT-3 can solve analogies based on meaningful relations
- GPT-3’s performance is limited to the information provided in its local context
- GPT-3 lacks long-term memory and physical understanding of the world
- GPT-3 exhibits a general capacity to identify and generalize relational patterns
- GPT-3’s analogical capacity is often considered the core of human intelligence
- GPT-3’s analogical capacity may be due to sheer size and diversity of training data
- GPT-3’s analogical capacity may be due to similarity and indirection of transformer architecture
- GPT-3’s analogical capacity is fundamentally different from human intelligence
- GPT-3’s analogical capacity is parasitic on natural human intelligence
Methods
Code availability
- Code for simulations available on GitHub
- Data from human behavioral experiments available on GitHub
Gpt-3
- Queried GPT-3 through OpenAI API
- Used text-davinci-003 model instance
- Performed additional experiments with davinci and text-davinci-002
- Temperature set to 0
- Max tokens set to 10 for Digit Matrices, 20 for letter string analogies, 10 for four-term verbal analogies, and 256 for story analogies
- Used log probabilities to evaluate GPT-3 on multiple-choice problems
Digit matrices
- Two major problem categories: transformation and logic
- Transformation problems had 1-5 rules
- Logic problems had 1 rule
- Transformation rules: constant, distribution-of-3, progression
- Logic rules: OR, XOR, AND
- Spatial position of elements aligned or permuted
- 6 one-rule subtypes, 6 two-rule subtypes, 10 subtypes for three-rule, four-rule, five-rule, and logic problems
- 100 instances of each subtype (except progression)
- Distractors generated using different methods for transformation and logic problems
- 43 participants in first experiment, 47 in second
- First experiment: 32 problem subtypes in random order
- Second experiment: 42 problem subtypes in order of increasing complexity
Story analogies
- Story analogy problems were tested in OpenAI playground
- Materials were taken from two sources
- Responses were not edited or shortened
- Figure S1 shows transfer from few-rule to many-rule Digit Matrix problems
- Text-davinci-002 did not show the same contextual effects as text-davinci-003
- Text-davinci-002 was not able to generalize from few-rule to many-rule problems
- Performance decreased significantly on four-rule and five-rule problems
S1 solutions to example matrix reasoning problems
- Solution to visual matrix reasoning problem in Figure 1a is option 5
- Solution to Digit Matrix problem in Figure 1b is option 7
- Solutions to problems in Figure 2 are in Table S1
S2 story analogy results
- Evaluated analogical reasoning in natural language problemsolving
- GPT-3 responses presented in bold text
S2.1 solution to radiation problem in isolation
- GPT-3 proposed a solution to a radiation problem
- Solution involves using brachytherapy, which involves placing a radioactive source directly into or near the tumor
S2.2 solution to radiation problem following general story
- Genie is transferring jewels from one bottle to another
- Target problem involves transferring gumballs from one bowl to another
- Genie uses a staff to stretch from one bottle to the other
- Target problem uses materials provided to transfer gumballs
- Source story and target problem both involve transferring something from one place to another
S2.3 solution to radiation problem with distracting stories
- GPT-3 proposed a solution to the radiation problem when presented with a general story and two distracting stories.
- GPT-3 did not identify the convergence solution in this case.
- The Wine Merchants story is about two merchants competing to bring a barrel of wine to a rich man.
- The General story is about a general who divides his army into small groups to capture a fortress.
- The Identical Twins story is about two twins who devise a plan to win a race.
- The target problem is a doctor faced with a patient suffering from an inoperable tumor.
- The proposed solution is brachytherapy and stereotactic radiotherapy.
- Brachytherapy involves placing a radioactive source directly into the tumor.
- Stereotactic radiotherapy involves using a machine to deliver a high-intensity beam of radiation to the tumor from outside the body.
S2.4 solution to radiation problem with distracting stories and prompt
- GPT-3 did not propose a solution to the radiation problem based on the analogy with the general story
- A prompt was used to encourage GPT-3 to consider the previously presented stories when generating its solution
- GPT-3 correctly identified the convergence solution and identified the general story as the relevant source
- The doctor could use the same tactic as the general in the second story to divide the rays into small groups and send each group down a different path to the tumor
S2.5 solution to gumball problem in isolation
- GPT-3 proposed a solution to the gumball problem
- Solution involves using materials provided: aluminum walking cane, posterboard, cardboard tube, scissors, string, tape, paper clips, and rubber bands
- Steps to solution: cut posterboard, tie string to tube and cane, place tube in bowl, use paper clips to secure tube, use rubber bands to secure tube to cane, pull cane towards you with string to transfer gumballs
S2.6 solution to gumball problem following magic staff story
- GPT-3 proposed a solution to the gumball problem involving a magic staff
- Children identified a solution involving an aluminum walking cane
- GPT-3 identified the high-level analogy between the source story and the target problem
- GPT-3 was tested on matrix reasoning problems, digit matrices, letter string analogies, and verbal analogies
- GPT-3 matched or exceeded human performance on all tests
- GPT-3 was able to generalize the structure inferred from few-rule problems to more complex many-rule problems
- GPT-3 was more reliable at identifying the successor-to-predecessor mapping than humans
- GPT-3 was more likely to produce a response involving a successor relation when primed with a context problem